There are many ways to optimize your website for local search so you can be found for multiple locations.
Just as there are many ways to optimize, so there are a variety of penalties lurking if you follow bad practices that egregiously violate Google’s guidelines.
By keeping a thorough inventory of your local SEO efforts, you will be able to avoid duplication and ensure high-quality implementation of all local SEO for your clients.
In addition, by learning the ins and outs of local SEO, you will be able to help yourself by creating your own winning strategy, rather than copying your competition and hoping you don’t get penalized by shady SEO tactics.
What Does Local SEO Look Like Today?
It should go without saying that legitimate businesses are more likely to have a chance to rank in Google local search as opposed to businesses that are less than legitimate.
This means a business with a winning product or service—something so compelling that helps the user accomplish what they are looking for, which matches the intent behind their query.
Don’t engage in any tactics that would be considered foul play: things like buying fake likes, reviews, or comments.
These will not help your business and, in fact, could lead to major issues with your SERP performance down the line.
Likely, local SEO will continue to be focused on citations as links, great-quality local content, and achieving sufficiently amplified traction across local news and media.
Although new factors could eventually be implemented, including entity-based local algorithm adjustments, and voice search playing a part (although this is still up for debate).
“Near me” searches have also increased recently, so it will be important to focus your local strategy on optimizing for “near me” queries.
Accuracy in Your Business Listings Is Also Important
Make sure all of your business listings match up with the NAP citations on your own site—punctuation, exact appearance, etc.
All of this plays a part in ensuring the accuracy of your business listing.
If something’s off, there could be difficulties locating your business, and in the algorithm’s interpretations of your on-site local SEO.
In other words, it could cause some confusion regarding where your business is really located.
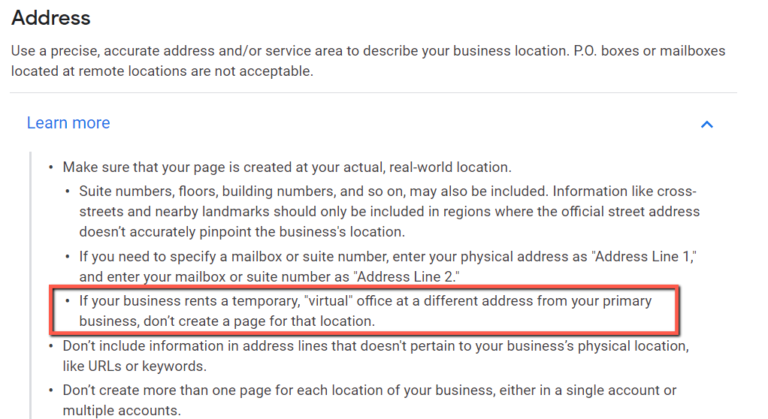
Don’t Use ‘Virtual Office’ Locations
Common techniques for local SEO in service industries include using virtual office locations, where the business will buy a virtual office, rent it, and implement it in their local SEO Google My Business listings.
Google recently made a GMB guideline clearer about the legalities of virtual offices as they relate to Google’s terms—and the news is not great.
I myself have had clients in the past who have been wiped off of Google Maps for ignoring this guideline because, quite simply, their competitor likely outed them in a spam report.
This little-known guideline for GMB says that you should not use Virtual Office locations as part of your strategy.
The only time you can use an off-site location is if it is fully-staffed during business hours.
This can have serious, negative consequences for your site, including and up to complete removal of your GMB listing if you are found out:
If this is a significant part of your Google My Business optimization strategy, you need to get rid of it now before you suffer consequences (if you are not already suffering consequences for breaking this rule).
Make Sure Your Business Shows Up in the Knowledge Panel
Local structured data is important to achieving a knowledge panel about your business in the SERPs.
Make sure:
- This structured data is added properly.
- That it validates in Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool.
- That there are no issues when it is indexed.
Here are some guidelines for implementing local SEO Schema: How to Use Schema for Local SEO.
It will be very awkward if your business listing shows up with punctuation errors on Google when due diligence was not properly performed in the first place.
Assessing Your Competition & the Market

Performing the proper competitor research on local content and links will help you determine how you will attack a particular niche.
First off, let’s examine a niche that is all-too-often overlooked: personal injury lawyers.
Say we are putting together a local campaign that will eventually target the top cities in the states.
We need to assess the general market and target markets that will fit our budget.
If we have a $1 million+ budget, it makes sense to go after the larger markets like Los Angeles, San Diego, etc.
But, if our budget is smaller, we will not be able to go after some of the larger markets.
Assessing the market is important before assessing the local competition.
You are assessing its ease of ranking, as well as other factors including traffic.
Now, while I can’t cover every single type of site in existence, I am going to dive into factors to consider at the start of your local SEO campaign.
Perform Your Research at the Population vs. Dollar Budget Level
Every city is going to have its own population numbers, its own population characteristics, and its own buying cycles.
It is important to assess the population and size of the market for two reasons:
- Budget: You do not want to throw money away selling motorcycles to a market largely interested in sweaters.
- Identify trends so you can time your campaigns around these increased buying periods.
Assess Your Competition
In any local market, you’re going to have local companies competing with each other who offer the same products and services.
When you assess your competition, you are assessing the ease of ranking for a particular market.
When you examine your competition, it is important to look at their:
- Linking strategy.
- Content strategy.
- Website structure.
Linking Strategy
When it comes to a local SEO linking strategy, it is important that you embark on a strategy that is highly specific and locally targeted to your city.
Ranking in local is very different from ranking in organic search: ranking factors are dependent on how strong the signals on your site are for your business’s specific location.
This is where local directories come in handy: they can help you get links for your locations fairly quickly without much effort.
Other types of local links include links in the local newspaper’s website, links from any website in which the URL has your city name in it, and links from your local chamber of commerce.
It is critical to assess the quality of the website linking to you before you go after it to avoid issues down the road.
Your local linking campaign is all for naught unless you get a handle on Google’s quality guidelines to ensure your links are not in violation of guidelines.
It is essential to go for top-quality links if you want your local SEO campaign to show results.
In addition to all of the above, you need to consider how your competition is building links to their website.
Using several tools, you can assess what links your competition is going after on nearly a daily basis.
Content Strategy
In addition to linking strategy, on-page optimization is crucial.
When creating local content, you want to make sure your content is locally focused and highly optimized toward the local areas you are targeting.
For example, if you were targeting “Los Angeles personal injury lawyers” you would need to ensure your URL, title tags, meta description, meta keywords, H1s, H2s, content, and internal links are optimized surrounding this keyword phrase.
If you want to get hyper-local, using a geolocation tag is important as well.
This is incredibly important when optimizing for your local on-site signals: do not forget to include the address of the location of your business on-page in text form.
This means: not in a graphic, not in a video, but in text form only.
Although Google crawls images, do you want to take the random chance that Google is not going to read that local ranking signal properly because you did not optimize it properly?

And yes, I know you are all rolling your eyes at the “meta keywords” thing, but hear me out: there is a reason why I mention this.
Yes, Google and Yahoo have both stated that they do not use meta keywords for rankings.
Duane Forrester, former Senior Product Manager at Bing, stated this in the past:
“I’ll make this statement: meta keywords is a signal. One of roughly a thousand we analyze. Getting it right is a nice perk for us, but won’t rock your world. Abusing meta keywords can hurt you.”
Because of this, and the fact all search engines do things just a little bit differently, it is OK to at least populate some keywords into the meta keywords tag, but don’t go overboard to the point that you reveal your entire keyword strategy to your competitors.
Or, even worse, you end up being flagged as spam by improper use of this tag.
Because the search engines do not use it for ranking, don’t waste a ton of time here.
At best, spend a few minutes putting in some keywords.
Put in a few well-researched, targeted keyword phrases, but don’t spend a lot of time on the meta keywords tag. Proceed accordingly and with much caution.
What Does a Properly Optimized Local Page Look Like?
Let’s take a look at the structure of a page that has properly been optimized for local on-page SEO:
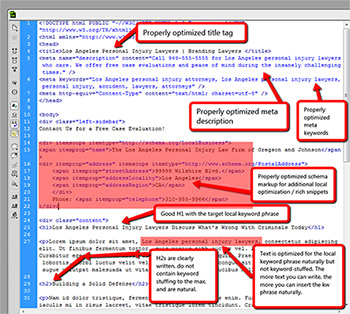
Properly Optimized Title Tag
This should be optimized to 50-60 characters in length, or you can take the newer approach of optimizing your title tag according to its pixel width.
Like the meta description below, the title tag should include the targeted location keyword phrase, the title of the page/article, and branding.
Ideally, a properly optimized title tag structure for most sites can look like:
Local keyword phrase in front | Title of Article | Company Name
Properly Optimized Meta Description
This should be optimized to approximately 156 characters.
The important thing is to make sure that you include your targeted location keyword phrase in the meta description.
While this will not improve rankings, it is an indirect improvement through having another point of relevance in your document and reinforces your targeted keyword use.
In addition, you can also include a local phone number as another local signal (note: local signal, not ranking signal) in addition to including a point of conversion.
There are a number of people who will call your page directly from the search results because it is fully convenient to do so from a mobile device.
Properly Optimized Schema Markup for Local Optimization or Rich Snippets
Surprise! Schema.org markup is important for better local SEO—but it is not a ranking factor.
It will allow you to appear in the rich snippet results of the Google search results for your business location—which is another way of getting your site “up there.”
But make no mistake—it is not a local ranking factor, just another avenue for ensuring that your site appears near the top results on the SERPs.
Good H1 with Targeted Local Keyword Phrase
A high-quality H1 header tag with your targeted local keyword phrase is necessary for local on-page optimization.
There are no real character lengths for this one.
Just make sure it is short, catchy (for drawing those pesky things called readers into your article—you do remember those people, right?), and includes your targeted local keyword phrase in such a way that it does not appear spammy to those aforementioned humans.
Optimize Actual Article Text for Your Local Keyword Phrase Naturally
Remember the days of 2002 in SEO, when keyword-stuffing was the hot SEO technique of the day?
Unreadable articles with keyword phrases stuffed in every other word plagued the web until Google rolled out its Florida update in 2003.
While it is important to optimize for specific keyword phrases in general organic SEO, on the flip side, it is also important to optimize for the local keyword phrase for local SEO.
When you have multiple pages dedicated to multiple locations, you need to change your focus on those pages to suit those locations.
For example: if you are performing optimization for one location, like “Orange County personal injury lawyers,” then you will want to make sure that your page is optimized for Orange County personal injury lawyers.
If you are optimizing for Long Beach personal injury lawyers as another location, the page should be optimized for Long Beach personal injury lawyers.
Change Your Local Content to Be Substantially Unique From Page to Page
It should go without saying that even though you are optimizing for different locations, you should not use the same content from page to page to optimize for each location properly.
Google’s Panda update has put a stop to all of that.
You must create quality content for each page that is being optimized for a different location to be successful.
I like to refer to it as “The Lazy SEO’s Way of Local SEO.”
They don’t want to put in the effort to write quality content, so they simply use the same content from page to page and change the location-specific parts, thinking that they will only get people from those locations on that page.
While, to some extent, that is true, it is not always the case.
It is, after all, only fair to take into account other visitors to your site who may visit other pages.
Maybe they are planning a trip and want to visit the other locations?
What if you were a visitor to a site that took this lazy approach and found the same content but only changed from page to page based on locality rather than the quality of the content?
You wouldn’t want to convert or buy from that site now, would you?
You would be thinking: “Why should I buy from a site who isn’t at least interested in their work enough to change their content for my location?”
It should go without saying: change your content strategy to compensate for quality content per locally optimized page.
This way, you avoid future algorithmic or, worse, manual penalties when Google manually views the site and you have to change all of that content anyway.
Consider Increasing the Quality of Your Local Content by Writing Longer Articles
In addition, you should also consider article length.
Longer articles tend to perform better (although this is not always the case—be sure to check your SERPs by using a competitor analysis tool to understand what Google is actually rewarding the top 10 results for).
Longer, more in-depth articles can lead to an overall lesser bounce rate, better reader retention rates, and overall better chances of going viral when they have the correct information written and conveyed to readers.
As a general rule, 400 words is considered an acceptable length for most competitive industries.
Again, this is going to be dictated by what



